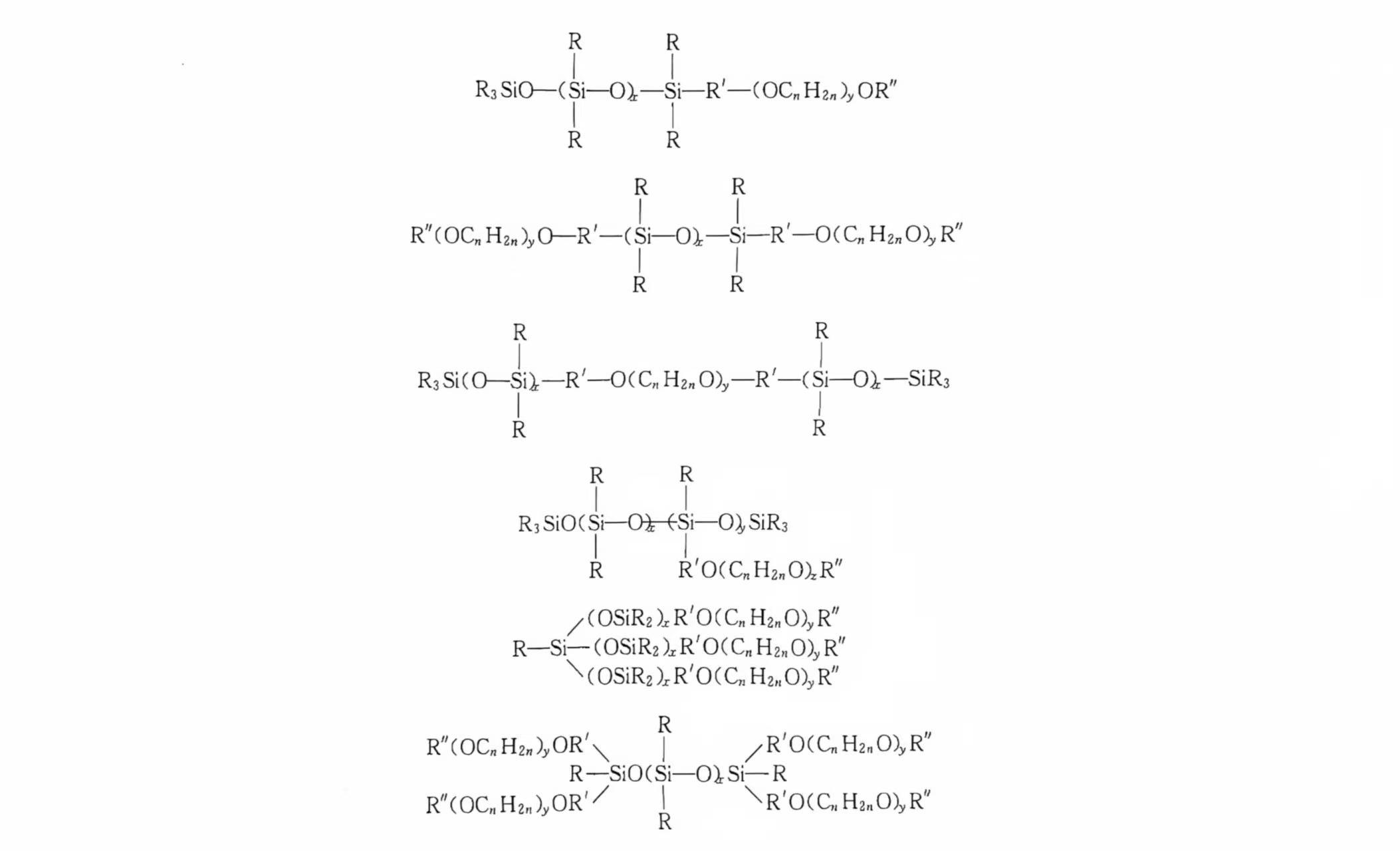
Foam silicone stabilizer is a category of surfactant and can be classified into non-silicone compounds and organosilicon compounds. Currently, the most widely used foam stabilizer in the industry is polyether-modified organosilicon surfactants (commonly named as "silicone oil"). Its primary structure consists of block or graft copolymers of polysiloxane and polyalkylene oxide. Due to their broad range of structural variations, with excellent performance, polyether-modified organosilicon surfactants have been widely adopted as foam stabilizers in the polyurethane foam industry.
There are various structures of organosilicon foam stabilizers; the structure of the silicone stabilizer, which is used in flexible foam, rigid foam, and high-resilience (HR) foam systems, differs. However, they generally contain repeating dimethylsiloxane units, ethylene oxide (EO) units, and propylene oxide (PO) units. One of the key functions of polyether-modified siloxane surfactants is to enhance the compatibility between PPU and the foam matrix, ensuring uniform dispersion of polyuria. This function is achieved through their polyether segments. The linkage between siloxane and polyalkylene oxide can take various forms, such as:
- AB-type linear block structure
- ABA-type linear block structure
- Single-branched and multi-branched structure
In the above structural formulas:
- R represents H, CH₃, C₂H₅, etc., most are methyl groups.
- R" represents H or an organic group.
- (CH₂O)ₙ typically refers to random copolymers of ethylene oxide (CH₂CH₂O) and propylene oxide [CH(CH₃)CH₂O].
- R' represents an alkyl group or may be absent.
Based on the nature of the chemical bond connecting the polysiloxane and polyalkylene oxide segments—the linkage between silicon, oxygen, and carbon atoms—organosilicon surfactants can be classified into two types:
- Si-O-C type (silicon-oxygen-carbon chain)
- Si-C type (silicon-carbon chain)
- The Si-C bond does not undergo hydrolysis, allowing the product to be stored for long periods without deterioration. Therefore, the silicone stabilizer used in rigid foam, high-resilience foam, is the Si-C type. Rigid foam stabilizer is typically polyether-polydimethylsiloxane copolymers, which are water-insoluble, non-hydrolyzable, and have emulsifying and nucleation effects. High-resilience foam stabilizers are also generally water-insoluble and non-hydrolyzable.
- The potency of polyester-based silicone surfactant should be significantly lower than polyether-based silicone surfactant. For cold-cured high-resilience foam systems and microcellular elastomers.
- Silicone stabilizers are generally colorless to pale yellow transparent liquids at room temperature.
- The dosage of silicone stabilizer ranges from 0.1% to 2.5%, typically between 0.5% and 1.5%. Higher dosages, finer cells, but may lead to closed-cell structures. In the same system, the dosage of silicone stabilizers for low-density foam is generally higher than high high-density formulations. For HR foams with high TDI content systems, a combination of foam stabilizers and foam modifiers may be used.
- In recent years, silicone stabilizers with low fogging, flame retardancy, and low emissions have been very popular.
Topwin is one of the leading professional manufacturers and solution providers with more than 20 years of experience, and has domestic top-level engineers in the silicone surfactant industry. Specializing in research and development, production, sales, and marketing of silicone-based special functional performance materials, Topwin also serves as a professional provider of technical services. Our products are mainly used in Polyurethane Foam, Corp Protection, Coatings and Inks, Leather & Textile, Silicone Release Coating for Paper and Film, Personal Care, and others.